What is a Pneumatic Pump? How It Works and Its Applications Explained
In the world of industrial machinery and fluid management, the pneumatic pump stands out as a critical component for various applications. According to Dr. Samantha Lee, an expert in fluid dynamics and pneumatic systems, "Pneumatic pumps are invaluable in numerous industries due to their efficiency and ability to handle a wide range of materials." This statement underscores the importance of understanding how pneumatic pumps operate and the benefits they offer.
Pneumatic pumps utilize compressed air to create a vacuum that draws in and expels fluids, making them suitable for transferring liquids, slurries, and even some gases. These pumps are widely used in manufacturing, food processing, and chemical industries, where precise and reliable fluid movement is essential. With the growing demand for automation and efficiency in industrial processes, the relevance of pneumatic pumps continues to increase, prompting a deeper exploration of their functions and potential applications.
As industries evolve and technology advances, the versatility of pneumatic pumps highlights their significance in modern operations. Understanding the mechanics behind these pumps will not only illuminate their operational capabilities but also showcase their transformative impact on achieving greater efficiency and productivity across various sectors.

What is a Pneumatic Pump?
A pneumatic pump is a device that utilizes compressed air to create a vacuum or to transfer fluids. It operates by converting the energy from compressed air into mechanical work, enabling the movement of liquids or gases in various industrial applications. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global pneumatic pump market was valued at approximately $3.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $5.1 billion by 2025, highlighting the increasing demand for efficient fluid handling techniques across multiple sectors.
These pumps are particularly favored in environments where electric pumps are impractical or pose safety risks due to flammable materials. The versatility of pneumatic pumps allows them to be used in applications ranging from petrochemicals to food processing. They are capable of handling a wide range of viscosities and can safely pump abrasive and corrosive substances. As stated in an article by Industrial Equipment News, the adoption of pneumatic pumps is expected to surge as industries prioritize safety, efficiency, and the reduction of maintenance costs, making them an essential component in modern manufacturing and processing systems.
Pneumatic Pump Applications and Usage Statistics
Principle of Operation for Pneumatic Pumps
Pneumatic pumps operate on the principle of converting compressed air into mechanical energy, which can then be used to move fluids. At the core of their functionality is a diaphragm or a piston that alternately expands and contracts within a chamber. When compressed air is introduced into the pump, it pushes down on the diaphragm or piston, creating a vacuum that draws in the fluid from the source. Upon release of the air pressure, the diaphragm or piston reverses its motion, expelling the fluid through the discharge outlet. This process can continue cyclically, making pneumatic pumps ideal for transferring liquids with varying viscosities.
The simplicity of their operation also contributes to the versatility of pneumatic pumps across different applications. They are commonly used in industries such as manufacturing, food processing, and pharmaceuticals, where cleanliness and reliability are paramount. The ability to handle corrosive or abrasive fluids without relying on electrical components further enhances their appeal. Additionally, the air-operated nature of these pumps allows for safe operation in hazardous environments, reducing the risk associated with electrical sparks. Thus, pneumatic pumps provide an efficient and effective solution for fluid transfer in a wide range of industrial applications.
Types of Pneumatic Pumps and Their Features
Pneumatic pumps are vital components in various industrial applications, utilizing compressed air to convert energy into mechanical work. There are several types of pneumatic pumps, each tailored for specific uses, making them versatile in manufacturing, construction, and other sectors. The two main types are diaphragm pumps and piston pumps. Diaphragm pumps are known for their ability to handle corrosive and viscous fluids, offering a leak-free operation which is critical in chemical processing industries. According to a recent market report by Research and Markets, the global diaphragm pump market is projected to reach $6.5 billion by 2025, underscoring their growing demand.
Piston pumps, on the other hand, are designed for high-pressure applications and are commonly used in the automotive and oil industries. These pumps show efficiency in transferring fluids at high flow rates, with the ability to generate pressures above 1000 psi, making them ideal for hydraulic systems. As highlighted by a study from MarketsandMarkets, the pneumatic pump market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 4.3%, indicating their crucial role in modern engineering.
Tips: When selecting a pneumatic pump, consider the fluid's viscosity and the required pressure output for optimal performance. Regular maintenance is also essential to ensure longevity and efficiency, preventing costly downtimes.
Common Applications of Pneumatic Pumps in Industry
Pneumatic pumps play a pivotal role in various industrial applications due to their efficiency and effectiveness in handling fluids. They are widely utilized in the automotive sector for power brake systems and paint spray systems, enabling tasks that require precise control over fluid flow.
Additionally, industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals rely on pneumatic pumps for moving materials safely and maintaining hygiene standards. Their ability to operate in hazardous environments makes them an indispensable tool in these sectors.
Moreover, the global market for pneumatic pumps is witnessing substantial growth, reflecting the increasing demand across numerous industries. For example, the air sampling pumps market is projected to grow from $59.34 million in 2025 to $82.22 million by 2032, indicating a healthy trend in related applications. This growth underscores the importance of pneumatic technology in enhancing operational capabilities and ensuring efficient resource management in industrial processes. As industries continue to evolve, pneumatic pumps are likely to find even more diverse applications, further solidifying their critical role.
Advantages and Limitations of Using Pneumatic Pumps
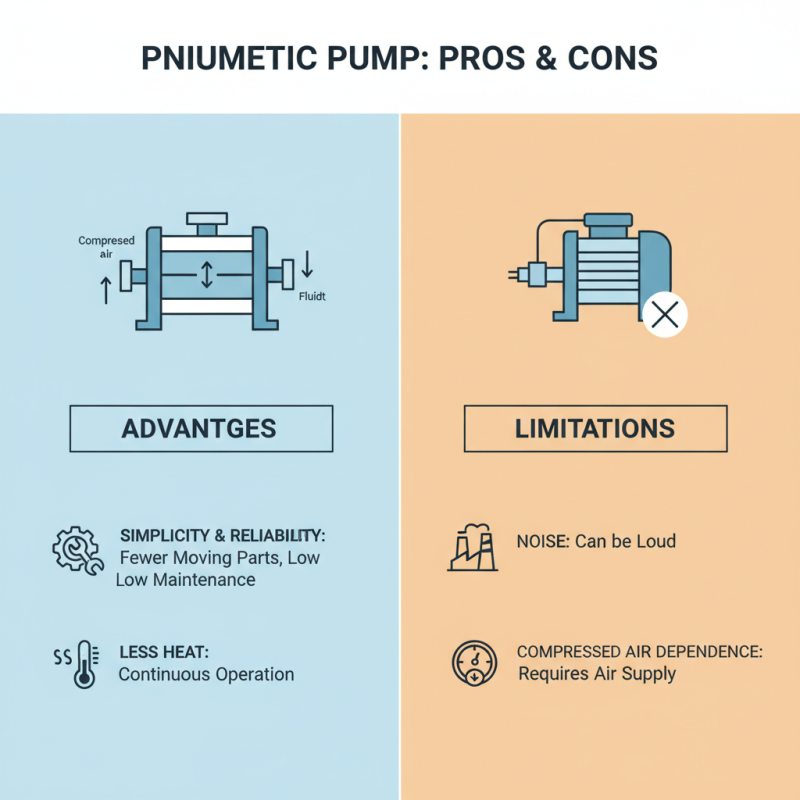
Pneumatic pumps, known for their efficient use of compressed air to move fluids, come with distinct advantages and limitations that users should consider. One notable advantage is their simplicity and reliability; pneumatic pumps have fewer moving parts compared to electric pumps, which reduces maintenance needs and enhances longevity. Additionally, they are less likely to overheat, making them suitable for continuous or prolonged operations in various environments.
However, using pneumatic pumps also has its drawbacks. They typically require a compressed air source, which can lead to higher operational costs if the air supply is not managed efficiently. Additionally, pneumatic pumps may have lower flow rates compared to electrical counterparts, making them less ideal for high-volume applications. Moreover, if not properly maintained, moisture in the compressed air could lead to corrosion and other operational issues.
**Tip:** When selecting a pneumatic pump, assess your specific application needs and consider the cost of compressed air versus the efficiency gains. Regular maintenance checks can also help extend the lifespan of your pump and ensure it operates at peak performance.
Related Posts
-

Understanding the Types of Fluid Pumps in Industrial Applications with Key Market Insights
-

Top 10 Benefits of Using Pump Systems for Efficient Fluid Management
-

2025 Top Chemical Injection Pumps: The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Best Options
-

Exploring Check Valve Innovations at the 2025 China Import and Export Fair
-
How to Optimize Your Injection Pumps for Maximum Efficiency and Performance
-
2025 How to Choose the Right Liquid Pump for Your Industrial Needs

Whether your solution requires a single pumping application or an expansive engineered system,
CheckPoint is committed to becoming your partner in excellence.